What Does The Macro Do?
 This macro takes the range selected by the user and export to PDF. This could be a chart, worksheet, range of cells or any type of Excel object.
This macro takes the range selected by the user and export to PDF. This could be a chart, worksheet, range of cells or any type of Excel object.
Prepare To Write Your Macro
Open the Visual Basic Editor. You can do this either by hitting ALT+F11 or hit the Developer Tab | Code Group | Visual Basic. Insert a new Module to store your VBA code. You can choose to insert a module in the current workbook or in your Personal Macro Workbook(PMW). If you choose to save your code in your Personal Macro Workbook then the code can be used in any Excel workbook. If you insert the code into the current workbook then you will be restricted to using the Macro in that workbook. In my example, I want to reuse the code so I have chosen to insert a module into my PMW. From the insert menu select Module. Ensure you have selected Personal.xlb from the project explorer window.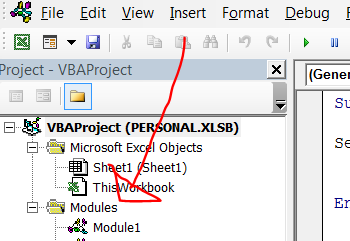
More Information On The Personal Macro Workbook
Macro Mondays – Create A Shortcut To Your Personal Excel Macro Workbook Macro Mondays -Creating and Updating Your Personal Macro WorkbookStarting The Macro.
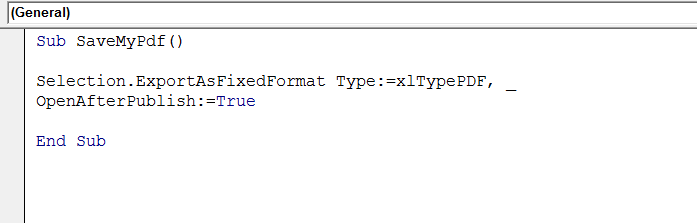
We need to start off the macro by inserting a New Module. Do this by selecting the Personal.xlsb workbook, then Insert Module. Type Sub then the name of your macro. In this example, I have called the macro SaveMyPdf. Notice that Excel will automatically enter the end text End Sub to end the Sub Routine. We simply need to enter the rest of the code between these two lines. [stextbox id=’info’] Sub SaveMyPdf() End Sub [/stextbox]Using The ExportAsFixedFormat Method To Export To PDF.
We use the ExportAsFixedFormat method in this Macro. This will allow us to export to PDF particular Excel Object files, (examples being a worksheet, charts) to another file format. In this case, it is a PDF file. This method has a number of parameters associated with it. I have summarised them below.type – This is the value which specifies the type of file format to export to.
- quality – the value that specifies the quality of the exported file.filename – this value determines the full file path of the newly created pdf if omitted the current folder is used
- includeDocProperties – flag as true to include document properties in the exported file; otherwise, false.
- ignorePrintAreas– set to true to ignore any print areas set when exporting; otherwise, false.
- from – The number of the page at which to start exporting. If this argument is omitted, exporting starts at the first page.
- to – The number of the last page to export. If this argument is omitted, exporting ends with the last page.
- openAfterPublish – true to display the file in the viewer immediately; otherwise, false.
- fixedFormatExtClassPtr – A pointer to an implementation of the IMsoDocExporter interface that enables the workbook to be saved in a different fixed format. For more information, see Extending the Office (2007) Fixed-Format Export Feature.
In this example, we only used the TYPE and OpenAfterPublish. [stextbox id=’info’] Selection.ExportAsFixedFormat Type:=xlTypePDF, _ OpenAfterPublish:=True [/stextbox]
Ending The Excel Macro.
Once all of the named ranges have been filled with colour the codes then end with the “End Sub” piece of code. This was already entered into the module for us when started the type the name of the macro. This is how to export to PDF.
[stextbox id=’info’]
End Sub
[/stextbox]

Do You Need Help With An Excel Problem?.
I am pleased to announce I have teamed up with Excel Rescue, where you can get help FAST.